本文共 5152 字,大约阅读时间需要 17 分钟。
CMOS摄像头测试
本小节使用的CMOS摄像头模块型号为Tronlong的TL2659,通过CAMERA总线进行视频采集并进行显示。
将摄像头模块镜头朝外,插到评估板CAMERA0或CAMERA1接口,亦可同时插入两个摄像头模块,硬件连接如下图所示。
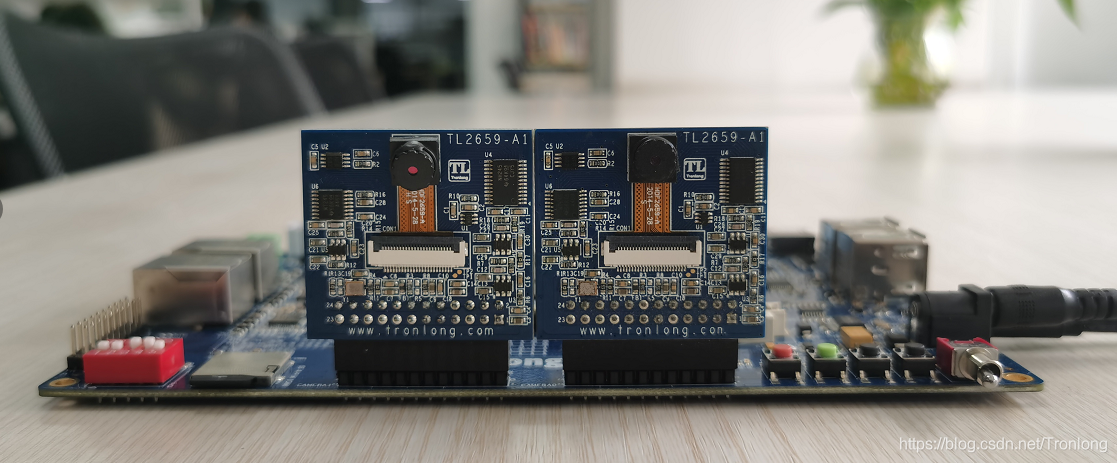
图 84
本小节测试程序由Linux Processor SDK自带,路径为”ti-processor-sdk-linux-rt-am437x-evm-04.03.00.05/example-applications/dual-camera-demo-1.0/dual_camera.sh”。
评估板连接7英寸LCD显示屏后,进入文件系统执行如下命令启动摄像头进行视频采集,可观察到显示屏进行视频实时显示。
Target# /usr/bin/dual_camera.sh
图 85
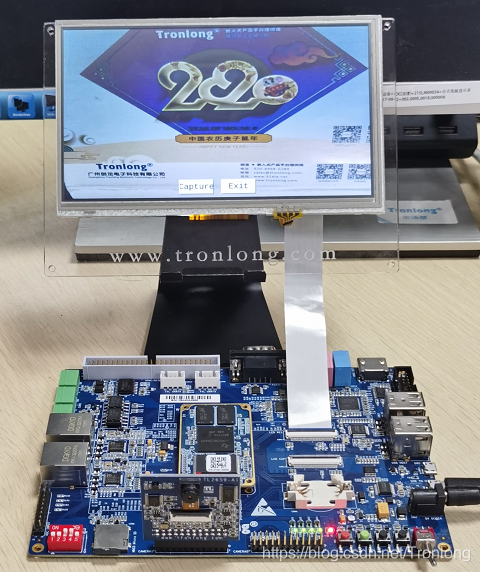

图 86
若插入两个摄像头则会显示画中画,如下图所示。可在显示屏上触控进行拍照、切换摄像头、退出等操作。按“Ctrl+C”即可退出程序。
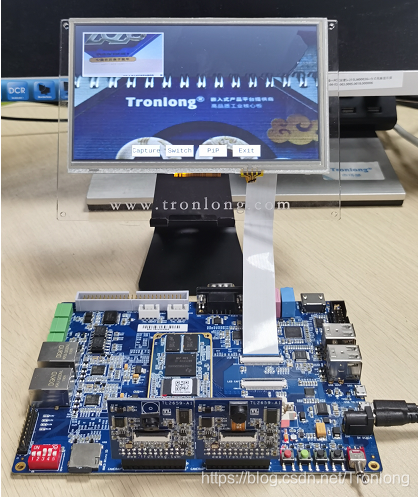
图 87
点击拍照后,图像保存将会在评估板文件系统”/usr/share/camera-images/”目录下。
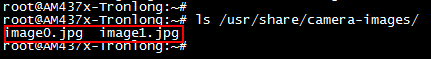
图 88
USB鼠标测试
内核已自带USB鼠标驱动,无须手动安装。进入评估板文件系统,将USB鼠标插入评估板任意USB接口,无线或有线鼠标均支持,串口终端将会打印如下类似信息。
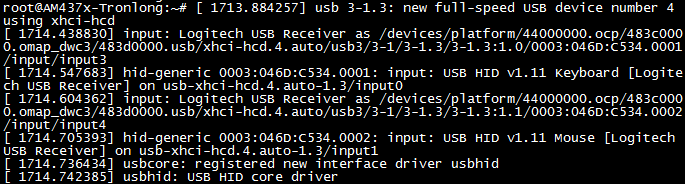
图 89
此时,可在LCD屏幕上发现鼠标光标,移动鼠标即可正常使用。
网络接口测试
评估板配备两个千兆网口,分别为RGMII ETH1和RGMII ETH2,网卡名字对应如下:
RGMII ETH1:eth0,默认网卡。
RGMII ETH2:eth1。
用网线将评估板对应网口连接到路由器,然后启动评估板。测试网络接口时,绿灯常亮、黄灯闪烁表示连接正常。
- 网络连通测试
进入评估板文件系统,执行如下命令获取IP以及查看网口配置信息。
Target# ifconfig
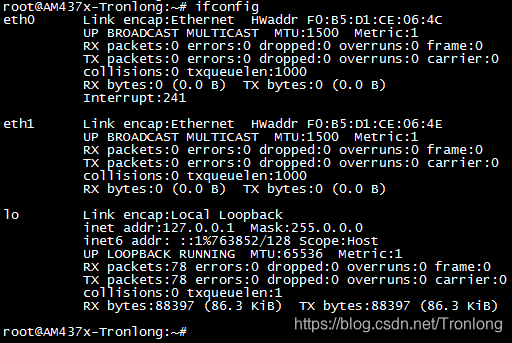
图 90
如果对应网卡没有自动获取到IP,请执行如下命令。
Target# udhcpc -i eth1
“-i”用于指定网卡,eth1为网卡名字,请根据实际情况修改。不加“-i”和网卡名字,则指默认网卡eth0。
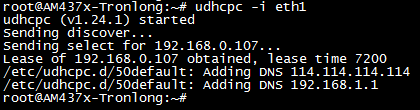
图 91
如有多个网口同时连接,请使用ifconfig命令关闭所有非当前测试网口,并打开当前测试网口。例如关闭eth1,打开eth0,命令如下。
Target# ifconfig eth1 down
Target# ifconfig eth0 up
网卡名字请根据实际情况修改,down表示关闭,up表示打开。如网口没有正常连接,请尝试先关闭网口再打开网口,直至打印“link becomes ready”信息表示已正常连接。
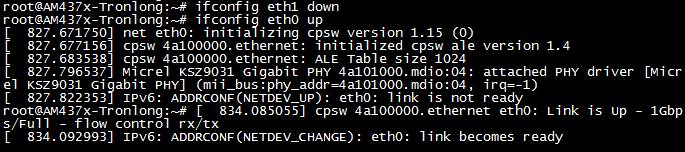
图 92
测试网口连接外网是否正常,以访问为例,执行如下命令,“-I”代表指定网口,不加“-I”则使用默认网卡。“Ctrl+C”终止ping命令。
Target# ping -I eth0
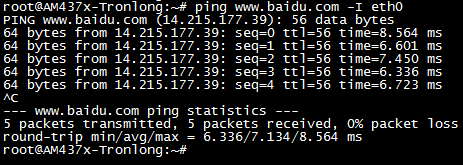
图 93
请执行如下命令查看网关。
Target# route
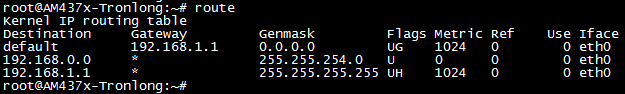
图 94
可看到此处网关为192.168.1.1,通过ping网关来测试内网连接功能是否正常,执行如下命令。
Target# ping 192.168.1.1
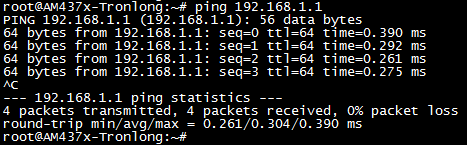
图 95
- 网络速度测试
以下使用Iperf工具测试评估板与PC机的网络通信速度。若未安装,可在Ubuntu中执行”sudo apt-get install iperf”安装。
在Ubuntu执行如下命令查看PC机IP地址并等待评估板连接。
Host# ifconfig
Host# iperf -s -i 1
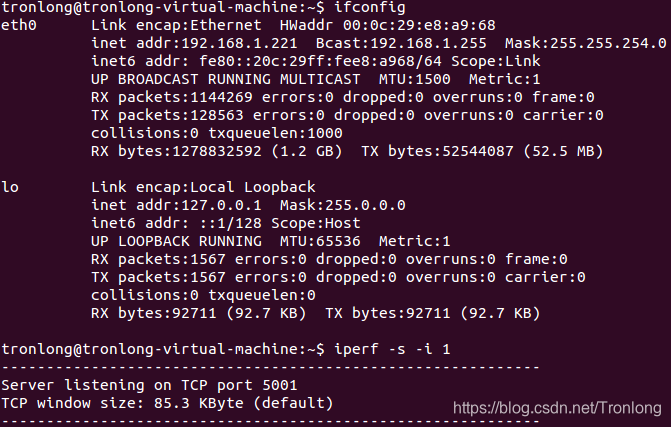
图 96
在评估板文件系统执行如下命令测试网络通信速度,命令中192.168.1.221为PC机IP地址。测试完成后,Ubuntu和评估板均会打印测试结果。不同测试环境,测试结果将会有所差异。
Target# iperf -c 192.168.1.221 -i 1
千兆网口RGMII ETH1速度测试结果大致如下。
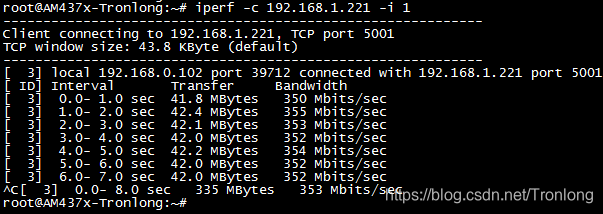
图 97
如使用RT-Linux内核进行测试,由于RT-Linux内核的cpsw默认采用IRQ中断模式,CPU系统资源占用较多,将对千兆网口的传输性能产生一定影响。使用RT-Linux内核进行测试,千兆网口RGMII ETH1速度测试结果大致如下。
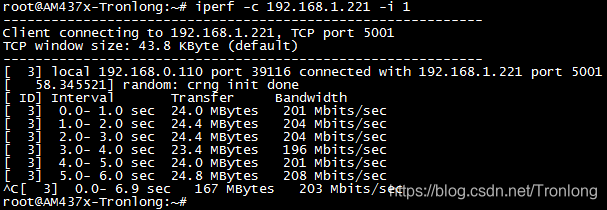
图 98
HDMI OUT接口测试
评估板默认通过LCD显示。请进入文件系统”/boot/”目录,将该目录下的tl437x-evm.dtb文件进行备份,再执行如下命令将tl437x-evm-hdmi.dtb文件重命名为tl437x-evm.dtb。评估板重启后,HDMI接口即可正常显示。
如需恢复为LCD显示,可将备份的文件重名为tl437x-evm.dtb,并重启评估板即可。
Target# cd /boot/
Target# cp tl437x-evm-hdmi.dtb tl437x-evm.dtb
Target# reboot
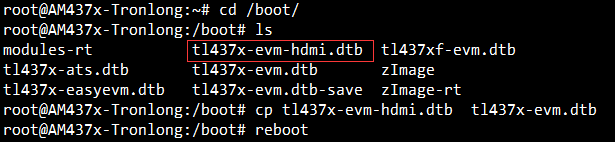
图 99
启动评估板后,可在HDMI显示屏看到图像输出,默认分辨率为1024*768@60,如下图所示。
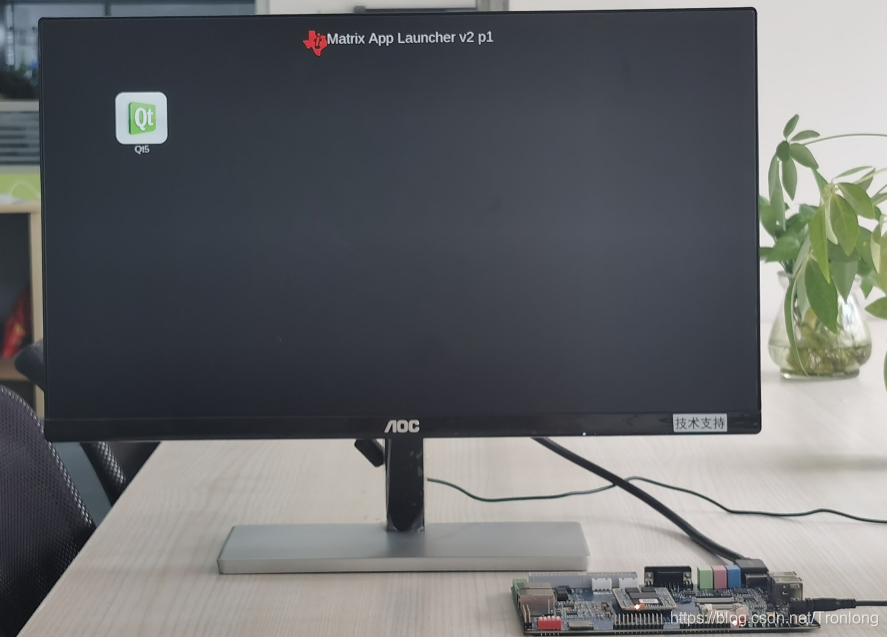
图 100
如需修改HDMI显示分辨率,可在U-Boot环境变量启动相关参数中添加HDMI分辨率设置,修改HDMI显示分辨率,命令如下。”1280x720MR-24@60”中的1280x720表示分辨率,60为帧率,请根据实际情况修改。
U-Boot# setenv optargs video=HDMI-A-1:1280x720MR-24@60
U-Boot# saveenv
U-Boot# boot
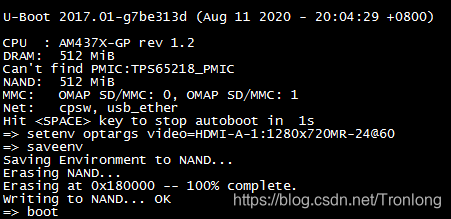
图 101
重启评估板后,即可看到HDMI显示屏分辨率已经成功设置为1280*720,如下图所示。

图 102
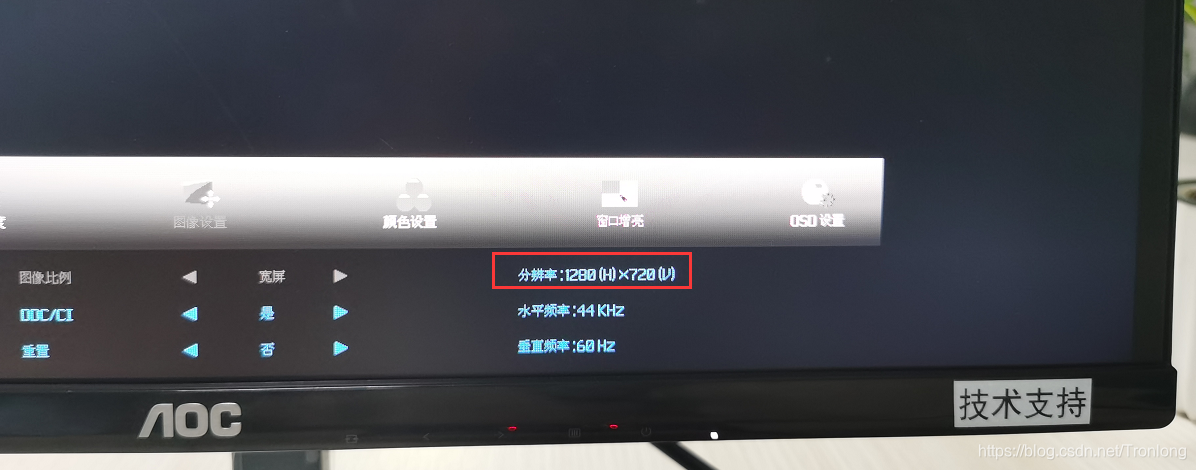
图 103
注意:DSS显示系统的像素时钟最大为100MHz,在1080P的分辨率下支持的最大帧率为35帧。如果设置的分辨率大于等于1080P35,可能会出现抖动现象,延迟可能比较明显。将分辨率改成1280*720@60,没有抖动现象,且延时不明显。
内部看门狗测试
watchdog-demo是一个内部看门狗测试程序,程序将读取系统预设看门狗等待时间,并重新设置看门狗等待时间为10秒,同时使用程序参数设置系统不喂狗时间。如果设置的不喂狗时间超过看门狗等待时间,系统将会重新启动。
将产品资料“4-软件资料\Demo\platform-test-demos\watchdog-demo\bin”目录下的可执行文件watchdog-demo拷贝到评估板文件系统任意路径,在可执行文件所在目录下执行如下命令设置不喂狗时间为12秒。10秒后,系统会重新启动。
Target# ./watchdog-demo 12
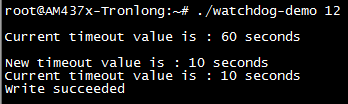
图 104
ADC数据采集测试
AM437x芯片内部含有2个8通道、12bit、867KSPS采样率的ADC,支持0~1.8V信号输入。TL437x-EVM评估板ADC0接口的通道0~3预留给电阻触摸屏使用,故测试从ADC0通道4开始。
以下为TL437x-EVM评估板ADC接口的原理图。
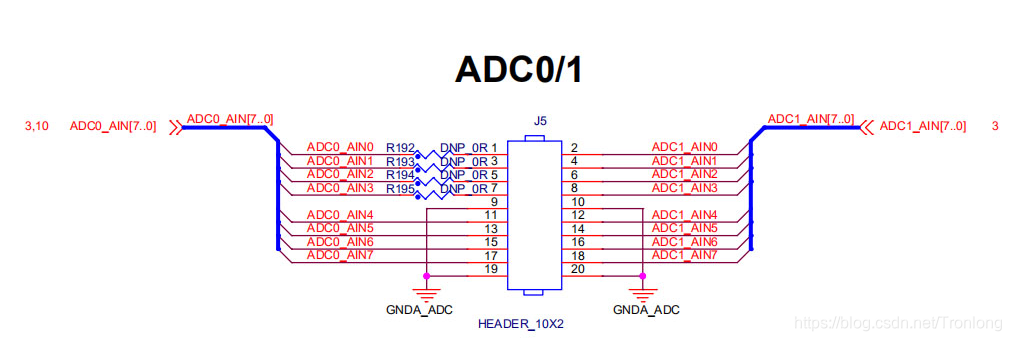
图 105
ADC参考电压为1.8V,待测电压信号不能超过1.8V,待测电压信号不能误接到GND,否则可能会损坏评估板。
将待测电压信号接到对应ADC输入通道,待测电压信号与评估板共地。进入评估板文件系统执行如下命令读取对应ADC通道的采样值,如下图所示。
Target# cat /sys/bus/iio/devices/iio:device0/in_voltage4_raw

图 106
device0指ADC0,device1指ADC1,in_voltage4_raw指通道4。
计算公式:实际电压值Vin=D*Vref/(2^n-1)。其中参考电压值Vref=1.8V,n=12,D为ADC采样值。
AUDIO音频测试
评估板的音频接口总共有三个:LINE OUT(绿色)、LINE IN(蓝色)、MIC IN(红色)。进入评估板文件系统,输入如下命令查看系统播放和录音设备,如下图所示。
Target# aplay -l
Target# arecord -l
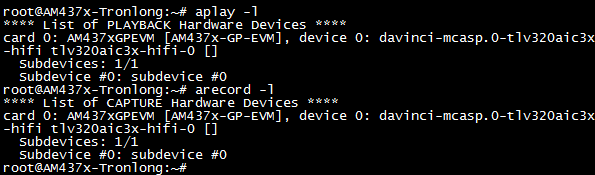
图 107
本小节使用Linux系统音频架构Alsa工具Amixer进行测试。进入评估板文件系统执行如下命令可查看Amixer命令说明。
Target# amixer --help
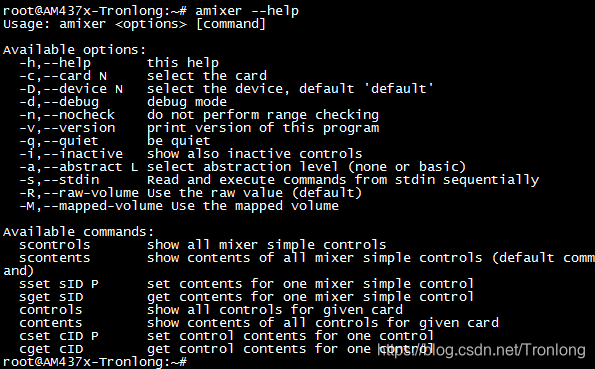
图 108
执行如下命令查看音频所有配置属性。
Target# amixer -i
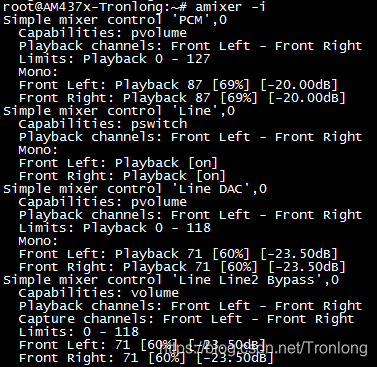
图 109
执行如下命令设置播放音量,AM437xGPEVM为声卡,音量最小为0,最大为127。
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset PCM 127
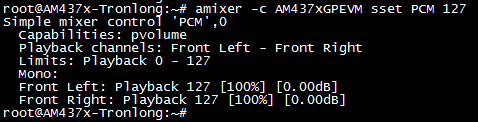
图 110
- LINE OUT音频输出测试
执行如下命令设置LINE OUT功能。
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Left Line Mixer DACL1' on
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Right Line Mixer DACR1' on
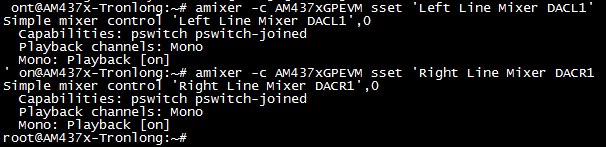
图 111
将电脑的小型喇叭或者耳机插入绿色LINE OUT音频孔,执行如下命令播放系统自带音频文件。
Target# aplay /usr/share/sounds/alsa/Front_Left.wav
Target# aplay /usr/share/sounds/alsa/Front_Right.wav
Target# aplay /usr/share/sounds/alsa/Front_Center.wav
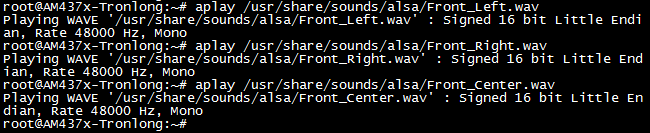
图 112
- LINE IN音频输入测试
请准备一条3.5mm两头均为公头的音频线,一端连接评估板的蓝色LINE IN音频接口,另外一端连接正在播放音频的播放器(手机或者MP4均可)。执行如下命令对LINE IN进行设置。
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Left PGA Mixer Line1L' on
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Right PGA Mixer Line1R' on
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Left PGA Mixer Mic3L' off
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Right PGA Mixer Mic3R' off
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'PGA' 40
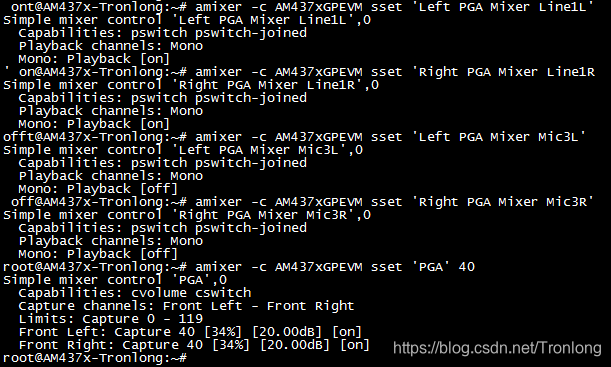
图 113
执行如下命令进行录音。
Target# arecord -f cd -r 44100 -d 10 -c 2 line_in.wav
命令注释:
- -f cd:以cd格式采样
- -r 44100:采样率44.1K
- -d 10:录音长度10s
- -c 2:2个声道
- line_in.wav:录音生成的音频文件

图 114
将电脑的小型喇叭或者耳机插入绿色LINE OUT音频孔,使用aplay命令将录制的音频文件进行播放。
Target# aplay line_in.wav
![]()
图 115
- MIC IN录音测试
将带麦克风的耳机的输入插头插到评估板红色MIC IN音频接口,耳机的输出插头插到评估板绿色LINE OUT音频接口。执行如下命令对MIC IN进行设置。
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Left PGA Mixer Line1L' off
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Right PGA Mixer Line1R' off
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Left PGA Mixer Mic3L' on
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'Right PGA Mixer Mic3R' on
Target# amixer -c AM437xGPEVM sset 'PGA' 40
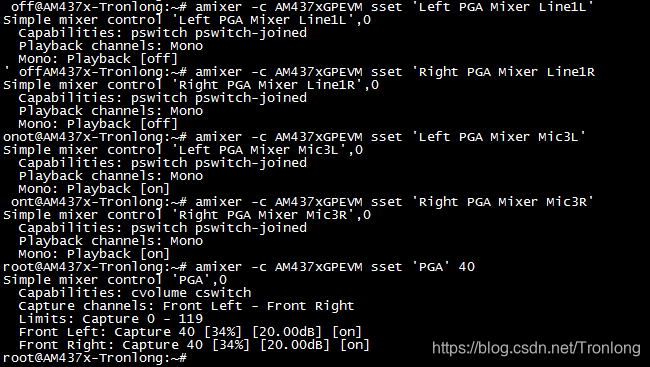
图 116
执行如下命令录制一段10秒的音频文件,并将其存放在当前路径下,如下图所示。
Target# arecord -f cd -r 44100 -d 10 -c 2 mic.wav
![]()
图 117
使用aplay命令播放录制的音频文件,耳机可听到录音播放声音,如下图所示。
Target# aplay mic.wav
![]()
图 118
转载地址:http://mdcb.baihongyu.com/